Food and Immunity: The Role of Nutrition in Strengthening Children’s Immune Systems
An unbalanced diet can lead to deficiency of one or more nutrients, which can affect your antibody and immunity production or activity. This can have a negative impact on your immune system. Thus, food plays a crucial role in enhancing our children’s immunity. There are five main nutritional components that significantly influence immune health: proteins, lipids (fats), carbohydrates, vitamins, and trace elements.

Proteins are essential for overall body function and maintaining a healthy microbiota. Protein deficiency can weaken the immune system, as proteins are made up of amino acids. These include essential amino acids, which the body cannot produce and must be obtained through diet, and non-essential amino acids, which the body can synthesize. Two important non-essential amino acids related to immune function are arginine and glutamine. Some studies suggest that arginine supplementation may benefit premature infants, while glutamine supplementation may be beneficial for those with low glutamine intake.
Lipids, particularly polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), are vital for children due to their high caloric density. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly important, with DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) playing a key role in immune support. The main dietary sources of DHA include oily fish. Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is the plant form of omega-3 fatty acids can also be useful to include into your diet. Nuts and seeds are a good source of ALA that you can have as a regular part of your diet. Another beneficial fat is conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), found in cow’s milk, dairy products, and breast milk, which also contributes to immune health.
Carbohydrates, especially prebiotics, are non-digestible carbohydrates that positively influence gut microbiota. Emerging studies indicate that a healthy gut microbiome can enhance immune function by increasing short-chain fatty acids and beneficial bacteria. Having a good and regular intake of fruits, vegetables, legumes and wholegrains can boost your prebiotic intake.
Micronutrients, including vitamins and trace elements, are critical for maintaining a robust immune system. Key vitamins that support immunity include:
- Vitamin A: Helps protect against infections.
- Vitamin B6: Important for making immune cells.
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid) and B12: Help the immune system work well.
- Vitamin C: Helps the body fight off germs.
- Vitamin D: Helps control immune responses.
- Vitamin E: Protects immune cells from damage.
Trace elements like zinc, copper, selenium, and iron are also vital for immune health.
- Zinc is essential for maintaining the immune system, with deficiencies linked to increased infection risk. While supplementation can help, it should only be pursued after appropriate testing. Meat, fish and seafood (especially oysters) are good sources of zinc.
- Copper supports the immune system, and deficiencies can lead to increased susceptibility to infections. Good sources include liver, fish, nuts, and cocoa.
- Selenium helps reduce inflammation and helps prevent sepsis, especially in critically ill patients. It can be found in liver, meat, and fish.
- Iron is crucial for immune cell growth. Deficiency can impair cognitive function and growth in children. Iron is available in heme (from animal products) and non-heme (from plant sources) forms, with heme iron being better absorbed. Pairing iron-rich foods with vitamin C can enhance absorption.
Not to forget, having plenty of fluids in the form of water to keep hydration levels up is essential for a healthy growing body. Sleep is also important to allow your child to rest. While sleeping, the body produces cytokines which helps fight infections. The amount of sleep a child need varies depending on their age – about 12-14 hours for your younger children and 8-10 hours for older children or teenagers.
To ensure optimal immune function, children should consume a balanced diet that includes all five food groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meat / meat alternative sources. This approach will help provide adequate amounts of protein, healthy fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and trace elements necessary to boost their immunity.
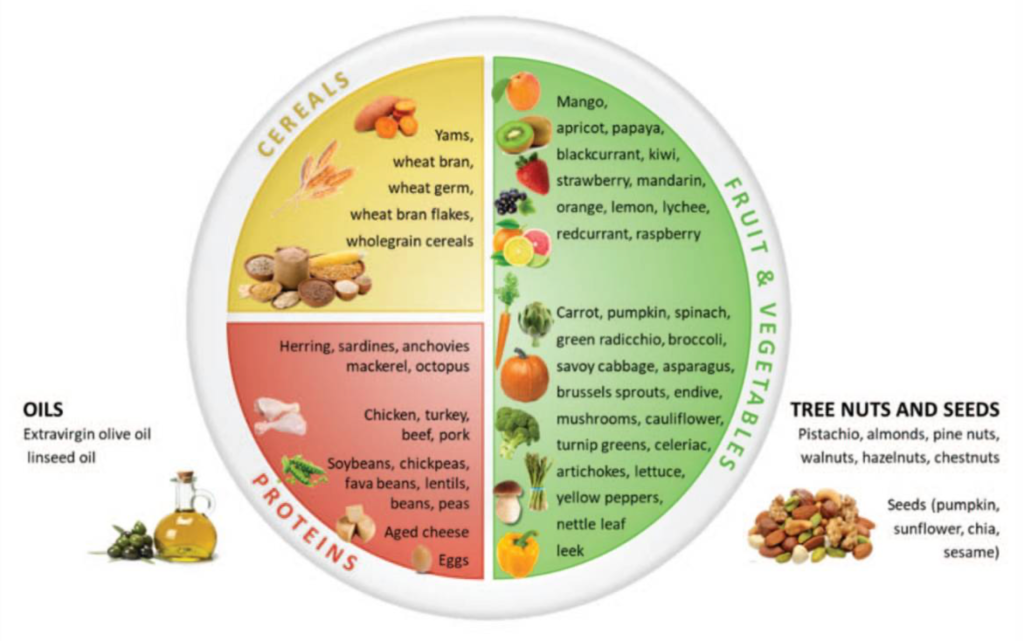
Photo sourced from this article